Windows Run
This section provides a detailed overview of executing commands on Windows devices.
All the actions can be run using either RDPRobot or DesktopRobot instances.
At the action’s call, the user can also specify a type of executor to use (for details see WinRunExecutionHandler).
DesktopRobot runs actions as a subprocess call by default, while RDPRobot runs all the actions
strictly via Windows Run window.
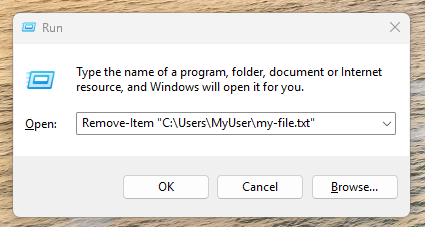
Calling WinRunRemoveFile via Windows Run window, in order to delete file on the provided path.
It is possible to run any of these actions as a .ps1 script, if the argument script_name is provided at the
action call, which will result in invoking the script with the action content, rather than calling the action
directly via run window (useful, for example, if the script exceeds the character limit for the run window)
Actions
- class aiviro.actions.windows_run.commands.WinRunOpenExplorer(*path: str | PureWindowsPath, config: ConfigWinRunActions | None = None, script_name: str = '')
Opens Windows Explorer at the specified path.
Warning
When specifying a drive, include the suffix :/. Otherwise, it is treated as a folder. If only : is specified, the path points to the current working directory of the drive. Always use X:/ for the root location of drive X.
- Parameters:
config – Configuration for the action
path – Path to a folder
- Example:
>>> import pathlib >>> import aiviro >>> from aiviro.actions.windows_run import WinRunOpenExplorer, ConfigWinRunActions >>> r = aiviro.create_rdp_robot_v2() >>> open_expl_action = WinRunOpenExplorer("c:/", "Users", "your_account")) >>> open_expl_action(robot=r) >>> # Here are some other examples on how to specify the path >>> WinRunOpenExplorer("c:/", "Users", "your_account")(r) >>> # also if required, the action can be called as a PowerShell script with for example timeout=10 >>> cfg = ConfigWinRunActions(timeout=10) >>> WinRunOpenExplorer(pathlib.PureWindowsPath("c:/") / "Users" / "your_account", config=cfg)(r) >>> WinRunOpenExplorer("c:/", pathlib.PureWindowsPath("Users", "your_account"))(r)
- class aiviro.actions.windows_run.commands.WinRunRemoveFile(*path: str | PureWindowsPath, recursive: bool = False, config: ConfigWinRunActions | None = None, script_name: str = '')
Removes a file or all files in a folder.
- Parameters:
path – Path to a file or folder.
recursive – If True, sub-folders are also removed.
- Example:
>>> import aiviro >>> from aiviro.actions.windows_run import WinRunRemoveFile >>> r = aiviro.create_rdp_robot_v2() >>> WinRunRemoveFile("c:/temp/file.txt")(r) >>> # path can be specified also as a pathlib.PureWindowsPath object >>> cfg = ConfigWinRunActions(as_admin=True)) >>> # runs recursive deletion of the folder "c:/Users/your_account" with admin privileges (set in the config) >>> WinRunRemoveFile(pathlib.PureWindowsPath("c:/") / "Users" / "your_account", recursive=True, config=cfg)(r) >>> # to run this action as a PowerShell script, the name of the file must be provided in the call >>> WinRunRemoveFile("c:/", pathlib.PureWindowsPath("Downloads", "my_screenshot.png"), script_name="my_script.ps1")(r)
- class aiviro.actions.windows_run.commands.WinRunStopProcess(*process_name: str, force: bool = False, restart_explorer: bool = False, config: ConfigWinRunActions | None = None, script_name: str = '')
Closes the specified application.
- Parameters:
process_name – Name of the process (e.g., “notepad”, “your_application.exe”).
force – If True, applications are force-closed; otherwise, they are gracefully closed.
restart_explorer – If True, Explorer is also restarted.
- Example:
>>> import aiviro >>> from aiviro.actions.windows_run import WinRunStopProcess >>> r = aiviro.create_rdp_robot_v2() >>> # stops notepad process and your_application.exe with force >>> WinRunStopProcess("notepad", "your_application.exe", force=True)(r) >>> # runs the action as a PowerShell script, which stops calc.exe and restarts explorer >>> cfg = ConfigWinRunActions(as_admin=True, ignore_length_limit=True) >>> WinRunStopProcess("calc.exe", restart_explorer=True, config=cfg, script_name="my_script.ps1")(r)
- class aiviro.actions.windows_run.commands.WinRunCloseAllOpenWindows(force: bool = False, config: ConfigWinRunActions | None = None, script_name: str = '')
Closes all open windows.
- Parameters:
force – If True, applications are force-closed; otherwise, they are gracefully closed.
- Example:
>>> import aiviro >>> from aiviro.actions.windows_run import WinRunCloseAllOpenWindows >>> r = aiviro.create_rdp_robot_v2() >>> WinRunCloseAllOpenWindows(force=True)(r)
- class aiviro.actions.windows_run.commands.WinRunCreateDirectory(*path: str | PureWindowsPath, open_after: bool = False, config: ConfigWinRunActions | None = None, script_name: str = '')
Creates a new directory.
- Parameters:
path – Path to the new directory.
open – If True, the newly created directory is opened after creation.
- Example:
>>> import pathlib >>> import aiviro >>> from aiviro.actions.windows_run import WinRunCreateDirectory >>> desktop_r = aiviro.create_desktop_robot() >>> WinRunCreateDirectory("c:/", "Users", "your_account")(robot=desktop_r)) >>> # Here are some examples on how to specify the path combined with other options >>> WinRunCreateDirectory(pathlib.PureWindowsPath("c:/") / "Users" / "your_account", script_name="my_script.ps1")(desktop_r)) >>> WinRunCreateDirectory("c:/", pathlib.PureWindowsPath("Users", "your_account"), open=True)(desktop_r)
- class aiviro.actions.windows_run.commands.WinRunMoveFile(source_path: str | PureWindowsPath, destination_path: str | PureWindowsPath, create_output_directory: bool = False, force: bool = False, config: ConfigWinRunActions | None = None, script_name: str = '')
Moves a file from the source path to the destination path.
- Parameters:
source_path – Source path of the file.
destination_path – Destination path of the file.
create_output_directory – If True, the output directory is created before the transfer.
force – If True, the command runs without asking for user confirmation.
- Example:
>>> import aiviro >>> from aiviro.actions.windows_run import WinRunMoveFile >>> r = aiviro.create_rdp_robot_v2() >>> WinRunMoveFile( ... source_path="c:/path/file.jpg", ... destination_path=pathlib.PureWindowsPath("c:/path/folder/file.jpg"), ... )(r) >>> # this action can be called as a PowerShell script as any of the `BaseWinRunAction` actions >>> WinRunMoveFile( ... source_path="c:/path/file.pdf", ... destination_path=pathlib.PureWindowsPath("c:/path/folder/file.pdf"), ... create_output_directory=True, ... force=True, ... script_name="my_move_script.ps1" ... )(r)
- class aiviro.actions.windows_run.commands.WinRunCopyFile(source_path: str | PureWindowsPath, destination_path: str | PureWindowsPath, recursive: bool = False, force: bool = False, config: ConfigWinRunActions | None = None, script_name: str = '')
Copies a file from the source path to the destination path.
- Parameters:
source_path – Source path of the file.
destination_path – Destination path of the file.
recursive – If True, performs a recursive copy.
force – If True, copies items that cannot otherwise be changed, such as copying over a read-only file.
- Example:
>>> import aiviro >>> from aiviro.actions.windows_run import WinRunCopyFile >>> r = aiviro.create_desktop_robot() >>> WinRunCopyFile( ... "c:/path/file.pdf", ... "c:/path/folder/file.pdf", ... )(r) >>> # if you want to copy recursively (all the subfolders), set recursive=True >>> WinRunCopyFile( ... "c:/path/file.pdf", ... "c:/path/folder/file.pdf", ... recursive=True, ... )(r)
- class aiviro.actions.windows_run.commands.WinRunCopyFileIntoClipboard(file_path: str | PureWindowsPath, config: ConfigWinRunActions | None = None, script_name: str = '')
Copies a file into the clipboard. When using
RDPRobotthe file is copied to remote (guest’s) clipboard and can be combined withtransfer_files_from_guests_clipboard(). When usingDesktopRobotthe file is copied to local clipboard.- Parameters:
file_path – Path to a file.
- Example:
>>> import aiviro >>> from aiviro.actions.windows_run import WinRunCopyFileIntoClipboard >>> # using rdp robot >>> r = aiviro.create_rdp_robot_v2() >>> WinRunCopyFileIntoClipboard("c:/path/file.pdf")(r) >>> r.transfer_files_from_guests_clipboard("some/local/dir/") ["some/local/dir/file.pdf"] >>> # using desktop robot >>> desktop_r = aiviro.create_desktop_robot() >>> # the file is now available in the clipboard >>> WinRunCopyFileIntoClipboard("c:/path/file.pdf")(robot=desktop_r) >>> # for example, it can be pasted >>> desktop_r.key_shortcut(aiviro.key.LEFT_CONTROL.KEY_V)
- class aiviro.actions.windows_run.commands.WinRunPasteFileFromClipboard(destination_dir: str | PureWindowsPath, create_destination_directory: bool = False, config: ConfigWinRunActions | None = None, script_name: str = '')
Pastes a file from the clipboard into the destination folder.
Note
When using RDPRobot the file is copied into the remote machine from the clipboard of the remote machine, not the host machine.
- Parameters:
destination_dir – Folder where the file will be pasted.
create_destination_directory – If True, the destination directory is created before the transfer.
- Example:
>>> import aiviro >>> from aiviro.actions.windows_run import WinRunPasteFileFromClipboard >>> r = aiviro.create_rdp_robot_v2() >>> cfg = ConfigWinRunActions(as_admin=True, use_likely_area=True, timeout=10) >>> WinRunPasteFileFromClipboard("c:/destination/dir", config=cfg)(r)
- class aiviro.actions.windows_run.commands.WinRunCopyValueIntoClipboard(value: str, config: ConfigWinRunActions | None = None, script_name: str = '')
Copies a value into the clipboard.
Note
When using RDPRobot the file is copied into the remote machine from the clipboard of the remote machine, not the host machine.
- Parameters:
value – Value to be copied.
- Example:
>>> import aiviro >>> from aiviro.actions.windows_run import WinRunCopyValueIntoClipboard >>> r = aiviro.create_rdp_robot_v2() >>> # simply sets 'value-to-clipboard' to the clipboard >>> WinRunCopyValueIntoClipboard("value-to-clipboard")(r)
- class aiviro.actions.windows_run.commands.WinRunCopyFileContentIntoClipboard(file_path: str | PureWindowsPath, config: ConfigWinRunActions | None = None, script_name: str = '')
Copies a file content into the clipboard - useful when simple values are present in the files.
Note
When using RDPRobot the file is copied into the remote machine from the clipboard of the remote machine, not the host machine.
- Parameters:
file_path – Path to a file, whose content will be copied.
- Example:
>>> import aiviro >>> from aiviro.actions.windows_run import WinRunCopyFileContentIntoClipboard >>> r = aiviro.create_rdp_robot_v2() >>> # file holds text 'an-important-message' which will be loaded into the clipboard >>> WinRunCopyFileContentIntoClipboard("c:/path/file.txt")(r)
- class aiviro.actions.windows_run.commands.WinRunInvokePowerShellScript(script_path: str | PureWindowsPath, config: ConfigWinRunActions | None = None, script_name: str = '')
Invokes a PowerShell script on the Windows machine.
- Parameters:
script_path – Path to the PowerShell script.
- Example:
>>> import aiviro >>> r = aiviro.create_rdp_robot_v2() >>> config = ConfigWinRunActions(as_admin=True, use_likely_area=True) >>> WinRunInvokePowerShellScript("c:/path/script.ps1")(r)
Executors
- class aiviro.actions.windows_run.execution_handlers.WinRunExecutionHandler(cmd: str, config: ConfigWinRunActions)
Base class for execution handlers for all the ‘WinRun’ actions.
- Parameters:
cmd – Path, name or command to execute
config – A configuration used for the execution. If not provided, a default configuration is used - for more details, see
ConfigWinRunActionsclass.
- class aiviro.actions.windows_run.execution_handlers.PSWinRunExecutor(cmd: str, config: ConfigWinRunActions)
Executes processes via Windows Run window and is available for both -
RDPRobotandDesktopRobot.
- class aiviro.actions.windows_run.execution_handlers.PSSubprocessExecutor(cmd: str, config: ConfigWinRunActions)
Executes processes using a subprocess module and is available only for the
DesktopRobot.
Configuration
- pydantic model aiviro.actions.windows_run.base.ConfigWinRunActions
Configuration used when executing created commands in all the ‘WinRun’ actions.
- Parameters:
timeout – Timeout for finding the Windows “Run” window.
as_admin – If True, commands are executed as an admin.
use_likely_area – If True, the area more likely to find the “Run” window is used (bottom left side of the screen).
sleep_time – Implicit sleep between sub-commands execution
sensitive_data – If True, typed text will be hidden in logs
ignore_length_limit – If True, the length of the command is not checked against the maximum limit.
keep_alive – If True, the process is kept alive after the command is executed.
process_args – List of arguments to pass to the subprocess.Popen constructor.